Large, heavy machines are a common sight in the construction world. Each is perfectly engineered to handle an intricate task efficiently. Pile drivers are a stand out among the diverse range of tools at a construction site. However, understanding the basics of pile driving and its benefits for your business requires some in-depth research.
In this article, we simplify the complex world of pile drivers and highlight their workings, types, and advantages.
What Does a Pile Driver Machine Do?
A pile driver is a heavy equipment machinery designed to push piles (support beams) deep into the ground using steady and consistent force application.
Piles are rigid, long structures that provide stable footing for a building’s foundations, helping carry the building’s weight all the way down to bedrock (stable underground rock bed).
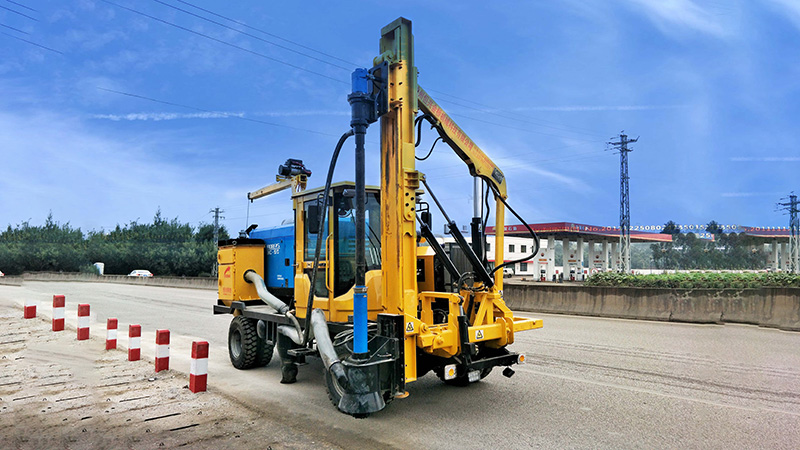

Quality pile-driving machines can easily push several hundred-foot-long piles into the ground in under a minute. Most pile structures are made of wood, steel, or concrete.
It is up to the pile driving machine’s operator to ensure appropriate force is applied so that the structural integrity of the structure remains intact.
The pile length can easily reach up to 150 ft. and weigh several metric tons, making these giant machines even more impressive.
How Does a Pile Driver Work?
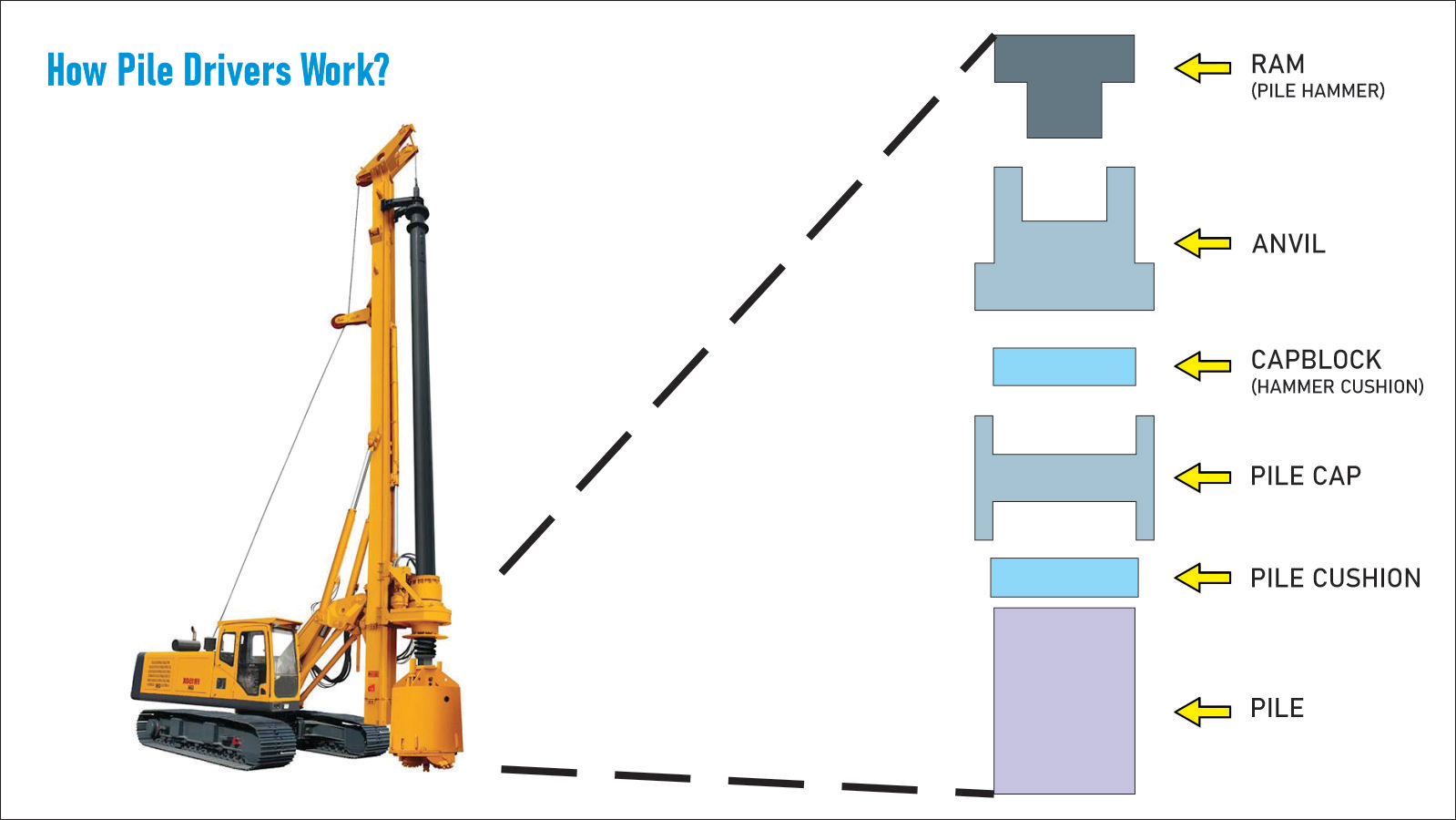
Understanding the basic working principles of a pile driver requires a firm grasp of the machine’s structure.
A pile driver machine has a similar look to a heavy-duty crane or truck. The main pile driver (crane arm) element rests on an industrial vehicle and a heavy ram, commonly referred to as a pile hammer, sits on the top of the crane.
Most pile drivers follow the same basic steps.
- The crane arm picks up the heavy pile and orients it vertically.
- A support at the base of the crane holds the pile steady.
- The hammer is lifted and dropped on a series of spacers (anvil, cushion, and pile cap).
- The spacers distribute the applied force evenly across the pile head.
- Piles can be installed flush to the ground or a few feet above ground level, depending upon the application.
These steps may change slightly depending on the type of pile-driving machine.
Types of Pile Drivers
Pile drivers are robust machines that can be configured in a few different ways.
A. Traditional Pile Drivers
The most popular pile-driving machines use vertical reciprocating pile hammers to drive the large structures into the soil.
Traditional hammers slide up and down a central pipe. A motor pulls the hammer to its highest point and drops it down, letting gravity do the rest of the work.
The motor that pulls the hammer up is usually powered by a diesel engine, hydraulic system, or steam power.
1. Diesel Hammer
Diesel hammers are the most widely available commercial pile-driving solution. Powered by a simple two-stroke engine, they offer good performance at a low cost and with minimum maintenance requirements.

With a diesel-powered pile driver, you increase your carbon footprint for operational convenience.
2. Hydraulic Hammer
Hydraulic hammers use motors to push an incompressible liquid through a series of tubes to generate pressure. The hydraulic system is specially designed to deliver a large force at the cost of energy efficiency.
Hydraulic impact hammers are the second most popular configuration for pile drivers.
3. Steam Hammer
A steam impact hammer utilizes boiling water to generate steam pressure. Newer pile drivers use the same basic principle of a steam impact hammer but replace the boiling water with a compressed air system to generate pressure.
Diesel and air hammers are generally more cost-effective than hydraulic hammer solutions.
B. Vibratory Pile Drivers
While traditional pile drivers work on the hammer-and-nail principle, vibratory pile-driving machines use vibrations to cut into the ground.

A motor is equipped with offset weights that induce vibration while spinning. The vibration gets transferred to the pile structure, slowly pushing it deep into the ground.
Unlike traditional crane-mounted diesel or hydraulic impact hammer systems, the vibratory hammer is generally mounted on an excavator base and can hold the pile structure from the side.
Vibratory pile drivers are preferred for their low noise output, which makes them particularly useful for night-time construction projects in urban areas.
| Pile Driver Type | Power | Equipment Cost | Cost of Operation | Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diesel Hammer | Medium | Medium | Medium | Convenient |
| Hydraulic Hammer | High | High | High | Powerful |
| Steam Hammer | Medium-Low | Medium | Low | Cost Effective |
| Vibratory Hammer | High | Very High | Medium-Low | Noiseless |
5 Huge Benefits of Pile Drivers
The conventional method of setting up a building’s foundation is to excavate several feet of soft soil and fill it up with concrete. Pile drivers offer a more convenient solution by eliminating the need for soil removal.
The following are some major benefits of foundation piling.
1. Material Flexibility
Standard foundation piling comes in three big material options: metal, concrete, and timber.
Steel piling has the highest depth penetration, concrete is the most environmentally friendly option, and timber is great for marine structures (piers, bridges, and boardwalks).
We discuss the advantages and disadvantages of various piling materials later in the article.
2. Application Adaptability
Driven piles can be modified to accommodate various environmental conditions. Pile shapes affect the amount of force required for driving, load capacity, longevity, and costs.
Similarly, pile materials determine the resistance to environmental damage.
Here are some of the most common variations on pile designs.
- Steel Piles – H-Pile, Pipe, Tapered, Sheet, etc.
- Concrete Piles – Square, Cylindrical, Sheet, etc.
- Timber Piles – Square, Cylindrical, Composite Reinforced, etc.
3. Time Efficiency
Pile drivers are incredibly time-efficient. The conventional system of digging up soil and refiling the site with concrete takes anywhere from a few weeks to several months. Contrarily, pile drivers can deposit large structures (piles) around the site in a matter of days.
4. Energy Efficiency
Excavating several feet of soil is a time and energy-consuming process. The machinery, fuel, and labor take up several times the resources of a standard pile driver.
While some applications may benefit from traditional foundation building, most others are better off going with pile drivers.
5. Cost Savers
Spending less time and less energy on a project will naturally lower your financial overhead. For construction businesses, pile drivers can help reduce lead time for projects, allowing them more work flexibility, better time management, and enabling expansion.
What Type of Piling Should You Use? Steel vs. Concrete vs. Timber!
Your choice of piling material and design is determined by several factors: budget, surface soil, building size, and weather conditions.
Let’s quickly examine the differences between the various piling options.
Friction vs. End Bearing Pile
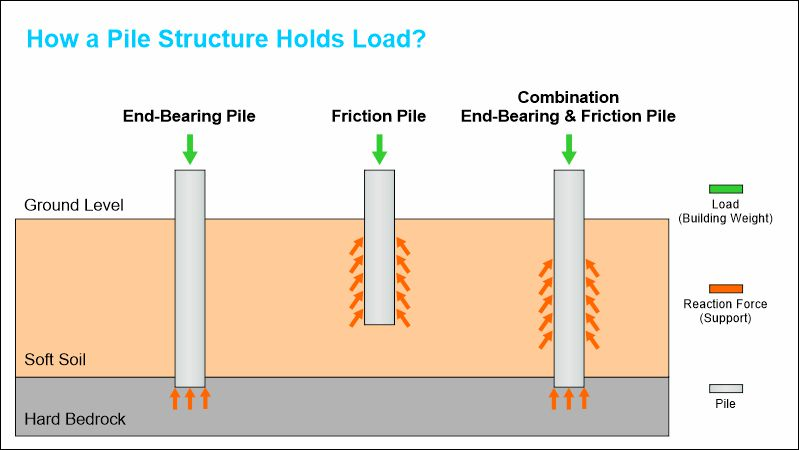
Standard load-bearing piles are driven deep into the soil until they hit bedrock. These piles sit on top of the bedrock and transfer the building weight onto the solid rock underneath the soil.
Alternately, friction piles are designed to fit pressure into the ground above the bedrock. Friction piles are kept in place by the friction induced by the compressive force of the surrounding soil.
Friction piles are shorter than end-bearing piles, saving on material costs and driving times. However, they are incompatible with soft soil areas and have a lower load-bearing capacity.
1. Steel Piling
Coated steel piling has excellent environmental resistance. It can withstand moisture, corrosion, and seismic damage. Steel is also compatible with vibratory hammers and offers better ground penetration.
Drawback
Steel is an expensive material that is difficult to cast, process, and store.
2. Timber Piling
Timber piling works well in compressed and wet soil. Depending on regional location, it has the lowest raw material cost. Their flexibility makes them a good option for above-ground applications, where occasional damage is inevitable.
Drawback
While it is a cost-effective solution, timber piling also has the most drawbacks. It can’t withstand heavy loads, is incompatible with hard ground, and is susceptible to corrosion and rot.
3. Concrete Piling
Concrete is a good middle ground between steel and timber solutions. It has excellent durability, good resistance, and is environmentally friendly. It is available in different shapes and can be reinforced with rebar. The material cost is also significantly lower than coated steel beams.
Drawback
The only drawback of concrete piling is its heavy weight. Casting concrete piling is easy, but transporting it is a whole other challenge.
| Types of Piling | Steel Pile | Timber Pile | Concrete Pile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | High | Low | Medium |
| Cost | High | Low | Low |
| Versatility | High | Low | Medium |
| Advantage | Corrosion Resistance Deeper Ground Penetration Sturdy | Good for Compressed or Wet Soil Cost Effective | Good Cost to Performance Environmental Friendly Sturdy |
| Drawback | Expensive | Prone to Rot | Difficult to Transport |
How to Choose a Pile Driver for Your Project?
The key to choosing the right pile driver for your business is all about analyzing your business’s regional requirements.
1. Regional Soil Assessment
Soil is one of the biggest deciding factors for any business investing in pile-driving machines.
Areas that experience regular heavy rain will have moist and soft soil. This makes pile installation easier, but corrosion chances are higher.
2. Size Requirements
Related to your regional soil situation, you may need to install longer piles so that they can reach the bedrock at the bottom. Smaller pile drivers will have a limit on the size of piles they can manage.
3. Budget Analysis
Heavy equipment is always going to be expensive, especially for larger machines. Shipping costs also scale exponentially with the size and weight of the machine. Be sure to have some extra overhead when allocating a budget.
4. Storage Considerations
Buying a large pile driver is just the first step in elevating your construction business. Proper storage and maintenance are essential to long-term safe operation.
FAQs
1. What Type of Machine is Used for Pile Driving?
Pile driver machines generally fall into two categories – Crane mounted drivers and excavator-mounted drivers.
2. How Deep Can You Drive Piles into the Ground?
Ground penetration capacities of piles are determined by soil softness and pile design. A metal H-pile can be driven up to 100 ft. (30m) into the ground.
3. Are Vibratory Pile Drivers better than Hydraulic Ones?
Vibratory pile drivers can hold onto the pile structure from the side and operate at a lower noise level.
4. What are Steel Sheet Piles?
Steel sheet piles have a corrugated design that is commonly used as a fence for waterfront structures.
Conclusion
Pile driving machines are an incredible testament to the advancements in modern manufacturing technology. These machines can hammer large, heavy piles into the ground in just a few minutes, saving customers time and money.
Piles are also a more efficient and effective way of building a foundation. It uses fewer resources and doesn’t destroy the natural soil at a construction site.
Beat the Competition, the Everstar!
Everstar has been working in the high-tech heavy machinery industry for over a decade. Our expertise and dedication have allowed us to establish a long and trust-based relationship with more than 6000 construction companies internationally.
Our Pile Drivers comply with various international safety standards, including ISO9001, CE, and CCC Certification. Our excellent after-sale services will help you set up your machine, train your operators, and provide in-depth guidance.
Stay ahead of the competition with the best-in-class products. Contact Us Now!